CAT Questions | CAT Geometry Questions
CAT Quantitative Aptitude | CAT Geometry Triangles , Circles
A CAT Geometry question that appears in the Quantitative Aptitude section of the CAT Exam broadly tests an aspirant on the concepts - Triangles, Circles, Quadrliaterals, Polygons & mixture of the above mentioned concepts. In CAT Exam, one can generally expect to get 4~6 questions from CAT Geometry. CAT Geometry is an important topic with lots of weightage in the CAT Exam. Make use of 2IIMs Free CAT Questions, provided with detailed solutions and Video explanations to obtain a wonderful CAT score. If you would like to take these questions as a Quiz, head on here to take these questions in a test format, absolutely free.
-
CAT Geometry: Obtuse Triangles - Integers
x, y, z are integer that are side of an obtuse-angled triangle. If xy = 4, find z.
-
CAT Geometry: Isosceles Triangles - Integers
How many isosceles triangles with integer sides are possible such that sum of two of the side is 12?
-
CAT Geometry: Triangles - Area
Sides of a triangle are 6, 10 and x for what value of x is the area of the △ the maximum?
-
CAT Geometry: Equilateral triangle and circle
Two circles are placed in an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. What is the ratio of the area of the smaller circle to that of the equilateral triangle
![Geometry - triangles: CAT Geometry Triangles Area]()
-
CAT Geometry: Triangles - Perimeter
Perimeter of a △ with integer sides is equal to 15. How many such triangles are possible?
-
CAT Geometry: Equilateral Triangle and Square
There is an equilateral triangle with a square inscribed inside it. One of the sides of the square lies on a side of the equilateral △. What is the ratio of the area of the square to that of the equilateral triangle?
-
CAT Geometry: Triangles - Integers
△ABC has integer sides x, y, z such that xz = 12. How many such triangles are possible?
-
CAT Geometry: Regular Polygon
ABCDE is a regular pentagon. O is a point inside the pentagon such that AOB is an equilateral triangle. What is ∠OEA?

-
CAT Geometry: Triangles Properties
△ has sides a2, b2 and c2. Then the triangle with sides a, b, c has to be:
-
CAT Geometry: Right Triangle Properties
Consider a right–angled triangle with inradius 2 cm and circumradius of 7 cm. What is the area of the triangle?
-
CAT Geometry: Regular Polygon
What is the ratio of longest diagonal to the shortest diagonal in a regular octagon?
-
CAT Geometry: Altitude of a Triangle
Find the altitude to side AC of triangle with side AB = 20 cm, AC = 20 cm, BC = 30 cm.
-
CAT Geometry: Regular Polygon
ABCDEF is a regular hexagon inscribed inside a circle. If the shortest diagonal of the hexagon is of length 3 units, what is the area of the shaded region.
-
CAT Geometry: Circles
A circle of radius 5 cm has chord RS at a distance of 3 units from it. Chord PQ intersects with chord RS at T such that TS = 1/3 of RT. Find minimum value of PQ.
-
CAT Geometry: Triangles - Area
Triangle has perimeter of 6 + 2√3 . One of the angles in the triangle is equal to the exterior angle of a regular hexagon another angle is equal to the exterior angle of a regular 12-sided polygon. Find area of the triangle.
-
CAT Geometry: Quadrilateral
Area of a Rhombus of perimeter 56 cms is 100 sq cms. Find the sum of the lengths of its diagonals
-
CAT Geometry: Quadrilateral
Rhombus has a perimeter of 12 and one angle = 120°. Find its area.
-
CAT Geometry: Triangles - Area
Circle with center O and radius 25 cms has a chord AB of length of 14 cms in it. Find the area of triangle AOB
-
CAT Geometry: Circles
Two mutually perpendicular chords AB and CD intersect at P. AP = 4, PB = 6, CP = 3. Find radius of the circle.
-
CAT Geometry: Triangles
Triangle ABC has angles A = 60° and B = 70°. The incenter of this triangle is at I. Find angle BIC.
-
CAT Geometry: Quadrilateral
Rhombus of side 6 cm has an angle equal to the external angle of a regular octagon. Find the area of the rhombus.
-
CAT Geometry: Circle, Square and Triangle
A circle inscribed in a square of side 2 has an equilateral triangle inscribed inside it. What is the ratio of areas of the equilateral triangle to that of the square?
-
CAT Geometry: Isosceles Triangles
An acute-angled isosceles triangle has two of its sides equal to 10 and 16. Find the area of this triangle.
-
CAT Geometry: Triangles - Area
Three equal circles are placed inside an equilateral triangle such that any circle is tangential to two sides of the equilateral triangle and to two other circles. What is the ratio of the areas of one circle to that of the triangle?
-
CAT Geometry: Triangle and Square
There is an equilateral triangle with a square inscribed inside it. One of the sides of the square lies on a side of the equilateral △. What is the ratio of the area of the square to that of the equilateral triangle?
-
CAT Geometry: Squares and Circles
Consider Square S inscribed in circle C, what is the ratio of the areas of S and C? And, Consider Circle Q inscribed in Square S, what is the ratio of the areas of S and Q?
-
CAT Geometry: Triangles - Area
Consider equilateral triangle T inscribed in circle C, what is ratio of the areas of T and C? Consider Circle C inscribed in equilateral triangle T, what is ratio of the areas of T and C?
-
CAT Geometry: Regular Octagon
Consider Regular Hexagon H inscribed in circle C, what is ratio of the areas of H and C? Consider Circle C inscribed in Regular Hexagon H, what is ratio of the areas of H and C?
- 2√3 : 3π , 3√3 : 4π
- 3√3 : π , 3√3 : 4π
- 3√3 : 2π, 2√3 : π
- √3 : π , √3 : 4π
-
CAT Geometry: Triangles
What is the distance between the orthocentre and the circumcenter of a triangle who sides measure 24 cm, 26 cm and 10 cm?
-
CAT Geometry: Circles and Triangles
Two circles with centres O1 and O2 touch each other externally at a point R. AB is a tangent to both the circles passing through R. P’Q’ is another tangent to the circles touching them at P and Q respectively and also cutting AB at S. PQ measures 6 cm and the point S is at distance of 5 cms and 4 cms from the centres of the circles. What is the area of the triangle SO1O2?
-
CAT Geometry: Circles
What is the circumference of the below circle given that AB is the diameter and XY is perpendicular to AB?

-
CAT Geometry: Circles
Find ∠PRB. Given
I. ∠BPQ = 22∘ and O is the centre of the circle
II. ∠RBP = 54∘ and chord PQ is parallel to AB

- Either I or II individually is sufficient
- Both I and II together are required
- One of the statements alone is sufficient
- Need more data
-
CAT Geometry: Triangles
The two sides of a triangle are 8 cm and 9 cm and one angle is 60∘. Which of the following can be the length of its third side?
I. √23 cm
II. √73 cm
III.(4.5 - √3.25) cm
IV. (4 + √33) cm
V. (9 + √13) cm
-
CAT Geometry: Quadrilateral
There is a set of parallel lines with x lines in it and another set of parallel lines with y lines in it. The lines intersect at 12 points. If x > y, find the maximum number of parallelograms that can be formed.
-
CAT Geometry: Polygon and Circles
There are 2 concentric circles, one big and one small. A square ABCD is inscribed inside the big circle while the same square circumscribes the small circle. The square touches the small circle at points P, Q, R and S. Determine the ratio of circumference of big circle to the polygon PQRS.
-
CAT Geometry: Quadrilaterals
If PQ || RS, find the value of x
-
CAT Geometry: Circles
A circle is inscribed in a semi-circle as shown:-
The radius of the circle possibly is:-
-
CAT Geometry: Circles
Two circles of radius 5 cm have a direct tangent PQ and an indirect tangent RS. Find the length of PQ if RS = 24 cm.
-
CAT Geometry: Circles and Triangles
In the below figure which of the following holds good?
-
CAT Geometry: Circles and Triangles
In the below figure, If \\frac{PR}{PQ}\\) = \\frac{PQ}{RQ}\\), then
- \\frac{PQ}{QR}\\) > 2
- \\frac{PQ}{QR}\\) = 2
- \\frac{PQ}{QR}\\) < 2
- can’t be determined
-
CAT Geometry: Triangles
A right angled triangle PQR is such that ∠PRQ = 90° and QR = 4 cm T is a point on QR such that PT = 3 cm, and perimeter of triangle PQT = Perimeter of triangle PTR Then, QT/TR takes the value:
-
CAT Geometry: Triangles
M and N are two points on the side PQ and PR of a triangle PQR respectively such that MNQR is a trapezium and MN:QR = 2:5. Find the ratio of the area of triangle PMN : Trapezium MNQR.
-
CAT Geometry: Triangles
In the below figure, ΔABC is right angled and AC = 100 cm. Also, AD = DE = EF = FC. Find the value of: BD2 + BE2 + BF2 (in cm2)
-
CAT Geometry: Triangles
The Olympics committee came up with a new rule. The flag of the gold medal winning team would be hoisted to the right (AB) at 5m. The flag of silver medal winning team would be hoisted to the left (PQ) at a height of 3m. The flag (MN) of bronze medal winning team would be hoisted at the point of intersection of the line joining the top of each of AB and PQ to the foot of other, as shown in the figure below. A and P are 8m apart. In a wrestling event, India won the bronze medal. Find the height at which the Indian flag was hoisted.
-
CAT Geometry: Polygons
The number of sides in a regular polygon is ‘T’ times the number of diagonals in it. What is the interior angle of this polygon in terms of T?
- 180 * \\frac{(T+2)}{(3T+2)}\\)
- 540 * \\frac{(T+2)}{(3T+2)}\\)
- 360 * \\frac{(T+2)}{(3T+2)}\\)
- 90 * \\frac{(T+2)}{(3T+2)}\\)
The Questions that follow, are from actual CAT papers. If you wish to take them separately or plan to solve actual CAT papers at a later point in time, It would be a good idea to stop here.
-
CAT 2023 Slot 3 - QA
Let \(\triangle A B C\) be an isosceles triangle such that \(A B\) and \(A C\) are of equal length. \(A D\) is the altitude from \(A\) on \(B C\) and \(B E\) is the altitude from \(\mathrm{B}\) on \(\mathrm{AC}\). If \(\mathrm{AD}\) and \(\mathrm{BE}\) intersect at \(\mathrm{O}\) such that \(\angle \mathrm{AOB}=105^{\circ}\), then \(\frac{A D}{B E}\) equals
- \(2 \sin 15^{\circ}\)
- \(\cos 15^{\circ}\)
- \(2 \cos 15^{\circ}\)
- \(\sin 15^{\circ}\)
-
CAT 2023 Slot 3 - QA
In a regular polygon, any interior angle exceeds the exterior angle by 120 degrees. Then, the number of diagonals of this polygon is
-
CAT 2023 Slot 2 - QA
In a rectangle ABCD, AB = 9 cm and BC = 6 cm. P and Q are two points on BC such that the areas of the figures ABP, APQ, and AQCD are in geometric progression. If the area of the figure AQCD is four times the area of triangle ABP, then BP : PQ : QC is
-
CAT 2023 Slot 2 - QA
A triangle is drawn with its vertices on the circle \(C\) such that one of its sides is a diameter of \(C\) and the other two sides have their lengths in the ratio \(a: b\). If the radius of the circle is \(r\), then the area of the triangle is
- \(\frac{a b r^2}{2\left(a^2+b^2\right)}\)
- \(\frac{a b r^2}{a^2+b^2}\)
- \(\frac{4 a b r^2}{a^2+b^2}\)
- \(\frac{2 a b r^2}{a^2+b^2}\)
-
CAT 2023 Slot 1 - QA
A quadrilateral ABCD is inscribed in a circle such that AB : CD = 2 : 1 and BC : AD = 5 : 4. If AC and BD intersect at the point E, then AE : CE equals
-
CAT 2023 Slot 1 - QA
In a right-angled triangle ABC, the altitude AB is 5 cm, and the base BC is 12 cm. P and Q are two points on BC such that the areas of ΔABP, ΔABQ and ΔABC are in arithmetic progression. If the area of ΔABC is 1.5 times the area of ΔABP, the length of PQ, in cm, is
-
CAT 2022 Slot 3 - QA
Suppose the medians BD and CE of a triangle ABC intersect at a point O. If area of triangle ABC is 108 sq. cm., then, the area of the triangle EOD, in sq. cm., is
-
CAT 2022 Slot 3 - QA
In a triangle \(\mathrm{ABC}, \mathrm{AB}=\mathrm{AC}=8 \mathrm{cm}\). A circle drawn with \(\mathrm{BC}\) as diameter passes through \(\mathrm{A}\). Another circle drawn with center at A passes through B and \(\mathrm{C}\). Then the area, in sq. \(\mathrm{cm}\), of the overlapping region between the two circles is
-
CAT 2022 Slot 3 - QA
The lengths of all four sides of a quadrilateral are integer valued. If three of its sides are of length 1 cm, 2 cm and 4 cm, then the total number of possible lengths of the fourth side is
-
CAT 2022 Slot 2 - QA
In triangle \(A B C\), altitudes \(A D\) and \(B E\) are drawn to the corresponding bases. If \(\angle B A C=45^{\circ}\) and \(\angle A B C=\theta\), then \(\frac{A D}{B E}\) equals
- \(\sqrt{2} \sin \theta\)
- \(\sqrt{2} \cos \theta\)
- \(\frac{(\sin \theta+\cos \theta)}{\sqrt{2}}\)
- 1
-
CAT 2022 Slot 2 - QA
Regular polygons A and B have number of sides in the ratio 1 : 2 and interior angles in the ratio 3 : 4. Then the number of sides of B equals
-
CAT 2022 Slot 2 - QA
The length of each side of an equilateral triangle \(\mathrm{ABC}\) is \(3 \mathrm{~cm}\). Let \(\mathrm{D}\) be a point on \(\mathrm{BC}\) such that the area of triangle \(\mathrm{ADC}\) is half the area of triangle \(\mathrm{ABD}\). Then the length of \(\mathrm{AD}\), in \(\mathrm{cm}\), is
-
CAT 2021 Slot 3 - QA
In a triangle ABC , ∠ BCA =50°. D and E are points on AB and AC, respectively, such that AD = DE. If F is a point on BC such that BD = DF, then ∠ FDE, in degrees, is equal to
-
CAT 2021 Slot 2 - QA
If a rhombus has area 12 sq cm and side length 5 cm, then the length, in cm, of its longer diagonal is
- \(\frac{\sqrt{37}+\sqrt{13}}{2}\)
- \(\frac{\sqrt{13}+\sqrt{12}}{2}\)
- √(37) + √(13)
- √(13) + √(12)
-
CAT 2021 Slot 2 - QA
Let D and E be points on sides AB and AC, respectively, of a triangle ABC, such that AD : BD = 2 : 1 and AE : CE = 2 : 3. If the area of the triangle ADE is 8 sq cm, then the area of the triangle ABC, in sq cm, is
-
CAT 2021 Slot 1 - QA
If the area of a regular hexagon is equal to the area of an equilateral triangle of side 12 cm, then the length, in cm, of each side of the hexagon is
-
CAT 2021 Slot 1 - QA
A circle of diameter 8 inches is inscribed in a triangle ABC where ∠ABC = 90°. If BC = 10 inches then the area of the triangle in square inches is
-
CAT 2021 Slot 1 - QA
Suppose the length of each side of a regular hexagon ABCDEF is 2 cm. It T is the mid point of CD, then the length of AT, in cm, is
-
CAT 2020 Question Paper Slot 3 - Geometry
In a trepezium ABCD, AB is parallel to DC, BC is perpendicular to DC and ∠BAD = 45°. If DC = 5 cm, BC = 4 cm, the area of the trepezium in sq. cm is
-
CAT 2020 Question Paper Slot 2 - Geometry
From the interior point of an equilateral triangle, perpendiculars are drawn on all three sides. The sum of the lengths of the perpendiculars is 's'. Then the area of the triangle is
-
CAT 2020 Question Paper Slot 2 - Geometry
Let C be a circle of radius 5 meters having center at O. Let PQ be a chord of C that passes through points A and B where A is located 4 meters north of O and B is located 3 meters east of O. Then, the length of PQ, in meters, is nearest to
-
CAT 2020 Question Paper Slot 2 - Geometry
Let C1 and C2 be concentric circles such that the diameter of C1 is 2cm longer than that of C2. If a chord of C1 has length 6 cm and is a tangent to C2, then the diameter, in cm of C1 is
-
CAT 2020 Question Paper Slot 1 - Geometry
A circle is inscribed in a rhombus with diagonals 12 cm and 16 cm. The ratio of the area of the circle to the area of the rhombus is
-
CAT 2019 Question Paper Slot 2 - Geometry
In a triangle ABC, medians AD and BE are perpendicular to each other, and have lengths 12 cm and 9 cm, respectively. Then, the area of triangle ABC, in sq cm, is
-
CAT 2019 Question Paper Slot 2 - Geometry
Two circles, each of radius 4 cm, touch externally. Each of these two circles is touched externally by a third circle. If these three circles have a common tangent, then the radius of the third circle, in cm, is
-
CAT 2019 Question Paper Slot 2 - Geometry
Let A and B be two regular polygons having a and b sides, respectively. If b = 2a and each interior angle of B is 3/2 times each interior angle of A, then each interior angle, in degrees, of a regular polygon with a + b sides is [TITA]
-
CAT 2019 Question Paper Slot 2 - Geometry
Let ABC be a right-angled triangle with hypotenuse BC of length 20 cm. If AP is perpendicular on BC, then the maximum possible length of AP, in cm, is
-
CAT 2019 Question Paper Slot 1 - Circles
In a circle of radius 11 cm, CD is a diameter and AB is a chord of length 20.5 cm. If AB and CD intersect at a point E inside the circle and CE has length 7 cm, then the difference of the lengths of BE and AE, in cm, is
-
CAT 2019 Question Paper Slot 1 - Geometry
AB is a diameter of a circle of radius 5 cm. Let P and Q be two points on the circle so that the length of PB is 6 cm, and the length of AP is twice that of AQ. Then the length, in cm, of QB is nearest to
-
CAT 2018 Question Paper Slot 2 - Geometry
On a triangle ABC, a circle with diameter BC is drawn, intersecting AB and AC at points P and Q, respectively. If the lengths of AB, AC, and CP are 30 cm, 25 cm, and 20 cm respectively, then the length of BQ, in cm, is (TITA)
-
CAT 2018 Question Paper Slot 2 - Geometry
A chord of length 5 cm subtends an angle of 60° at the centre of a circle. The length, in cm, of a chord that subtends an angle of 120° at the centre of the same circle is
-
CAT 2018 Question Paper Slot 1 - Geometry
In a circle with centre O and radius 1 cm, an arc AB makes an angle 60 degrees at O. Let R be the region bounded by the radii OA, OB and the arc AB. If C and D are two points on OA and OB, respectively, such that OC = OD and the area of triangle OCD is half that of R, then the length of OC, in cm, is
- \\frac{π}{4})\\frac{1}{2})
- \\frac{π}{6})\\frac{1}{2})
- \\frac{π}{4√3})\\frac{1}{2})
- \\frac{π}{3√3})\\frac{1}{2})
-
CAT 2018 Question Paper Slot 1 - Geometry
Given an equilateral triangle T1 with side 24 cm, a second triangle T2 is formed by joining the midpoints of the sides of T1. Then a third triangle T3 is formed by joining the midpoints of the sides of T2. If this process of forming triangles is continued, the sum of the areas, in sq cm, of infinitely many such triangles T1, T2, T3,... will be
-
CAT 2018 Question Paper Slot 1 - Geometry
Let ABCD be a rectangle inscribed in a circle of radius 13 cm. Which one of the following pairs can represent, in cm, the possible length and breadth of ABCD?
-
CAT 2018 Question Paper Slot 1 - Geometry
Points E, F, G, H lie on the sides AB, BC, CD, and DA, respectively, of a square ABCD. If EFGH is also a square whose area is 62.5% of that of ABCD and CG is longer than EB, then the ratio of length of EB to that of CG is:
-
CAT 2018 Question Paper Slot 1 - Geometry
In a circle, two parallel chords on the same side of a diameter have lengths 4 cm and 6 cm. If the distance between these chords is 1 cm, then the radius of the circle, in cm, is
-
CAT 2017 Question Paper Slot 2 - Geometry
Let ABCDEF be a regular hexagon with each side of length 1 cm. The area (in sq cm) of a square with AC as one side is
-
CAT 2017 Question Paper Slot 2 - Geometry
The base of a vertical pillar with uniform cross section is a trapezium whose parallel sides are of lengths 10 cm and 20 cm while the other two sides are of equal length. The perpendicular distance between the parallel sides of the trapezium is 12 cm. If the height of the pillar is 20 cm, then the total area, in sq cm, of all six surfaces of the pillar is
-
CAT 2017 Question Paper Slot 2 - Geometry
ABCD is a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle with centre O. If ∠COD = 120 degrees and ∠BAC = 30 degrees, then the value of ∠BCD (in degrees) is [TITA]
-
CAT 2017 Question Paper Slot 2 - Geometry
If three sides of a rectangular park have a total length 400 ft., then the area of the park is maximum when the length (in ft.) of its longer side is [TITA]
-
CAT 2017 Question Paper Slot 2 - Geometry
Let P be an interior point of a right-angled isosceles triangle ABC with hypotenuse AB. If the perpendicular distance of P from each of AB, BC, and CA is 4(√2 - 1) cm, then the area, in sq. cm, of the triangle ABC is [TITA]
-
CAT 2017 Question Paper Slot 1 - Geometry
From a triangle ABC with sides of lengths 40 ft, 25 ft and 35 ft, a triangular portion GBC is cut off where G is the centroid of ABC. The area, in sq ft, of the remaining portion of triangle ABC is:
-
CAT 2017 Question Paper Slot 1 - Geometry
Let ABC be a right-angled isosceles triangle with hypotenuse BC. Let BQC be a semi-circle, away from A, with diameter BC. Let BPC be an arc of a circle centered at A and lying between BC and BQC. If AB has length 6 cm then the area, in sq. cm, of the region enclosed by BPC and BQC is:
-
CAT 2017 Question Paper Slot 1 - Geometry
Let ABC be a right-angled triangle with BC as the hypotenuse. Lengths of AB and AC are 15 km and 20 km, respectively. The minimum possible time, in minutes, required to reach the hypotenuse from A at a speed of 30 km per hour is: (TITA)
The Questions that follow, are from actual XAT papers. If you wish to take them separately or plan to solve actual XAT papers at a later point in time, It would be a good idea to stop here.
XAT 2020 Question Paper - QADI
Two lighthouses, located at points A and B on the earth, are 60 feet and 40 feet tall respectively. Each lighthouse is perfectly vertical and the land connecting A and B is perfectly flat. The topmost point of the lighthouse at A is A’ and of the lighthouse at B is B’. Draw line segments A’B and B’A, and let them intersect at point C’. Drop a perpendicular from C’ to touch the earth at point C. What is the length of CC’ in feet?
XAT 2020 Question Paper - QADI
A rectangular field is 40 meters long and 30 meters wide. Draw diagonals on this field and then draw circles of radius 1.25 meters, with centers only on the diagonals. Each circle must fall completely within the field. Any two circles can touch each other but should not overlap.
What is the maximum number of such circles that can be drawn in the field?XAT 2020 Question Paper - QADI
XYZ is an equilateral triangle, inscribed in a circle. P is a point on the arc YZ such that X and P are on opposite sides of the chord YZ. Which of the following MUST always be true?
- XZ + YP = XY + PZ
- XP = YP + PZ
- XP + PZ = XY + YP
- XP = XY
- XP = XY + YZ
Choice B
XP = YP + PZXAT 2019 Question Paper - QADI
In the picture below, EFGH, ABCD are squares, and ABE, BCF, CDG, DAH are equilateral triangles. What is the ratio of the area of the square EFGH to that of ABCD?
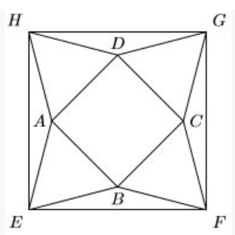
XAT 2019 Question Paper - QADI
What is the maximum number of points that can be placed on a circular disk of radius 1 metre (some of the points could be placed on the bounding circle of the disk) such that no two points are at a distance of less than 1 metre from each other?
XAT 2019 Question Paper - QADI
The figure below shows two right angled triangles ∆OAB and ∆OQP with right angles at vertex A and P, respectively, having the common vertex O, The lengths of some of the sides are indicated in the figure. (Note that the figure is not drawn to scale.) AB and OP are parallel. What is ∠QOB?
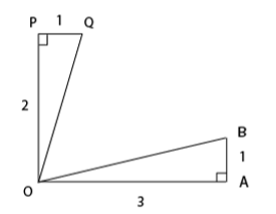
XAT 2019 Question Paper - QADI
Let ABC be an isosceles triangle. Suppose that the sides AB and AC are equal and let the length of AB be x cm. Let b denote the angle ∠ABC and sin b = 3/5. If the area of the triangle ABC is M square cm, then which of the following is true about M?
- M < \\frac{x^{2}}{4})
- M ≥ x2
- \\frac{3 x^{2}}{4}) ≤ M < x2
- \\frac{x^{2}}{2}) ≤M < \\frac{3 x^{2}}{4})
- \\frac{x^{2}}{4}) ≤ M < \\frac{x^{2}}{2})
XAT 2018 Question Paper - QADI
If the diagonals of a rhombus of side 15 cm are in the ratio 3:4, find the area of the rhombus.
XAT 2018 Question Paper - QADI
Two circles with radius 2R and √2R intersect each other at points A and B. The centers of both the circles are on the same side of AB. O is the center of the bigger circle and ∠AOB is 60°. Find the area of the common region between two circles.
The Questions that follow, are from actual IPMAT papers. If you wish to take them separately or plan to solve actual IPMAT papers at a later point in time, It would be a good idea to stop here.
IPMAT 2020 Sample Paper - IPM Rohtak Quants
A line from center to circumference of a circle is known as
IPMAT 2020 Question Paper - IPM Indore Quants
The number of acute angled triangles whose sides are three consecutive positive integers and whose perimeter is at most 100 is
IPMAT 2019 Question Paper - IPM Indore Quants
The sum of the interior angles of a convex n-sided polygon is less than \2019^{\circ}\\). The maximum possible value of n is
IPMAT 2019 Question Paper - IPM Indore Quants
The maximum distance between the point (-5, 0) and a point on the circle x2 + y2 = 4 is
IPMAT 2019 Question Paper - IPM Indore Quants
A chord is drawn inside a circle, such that the length of the chord is equal to the radius of the circle. Now, two circles are drawn, one on each side of the chord, each touching the chord at its midpoint and the original circle. Let k be the ratio of the areas of the bigger inscribed circle and the smaller inscribed circle, then k equals
IPMAT 2019 Question Paper - IPM Indore Quants
Points P, Q, R and S are taken on sides AB, BC, CD and DA of square ABCD respectively, so thatAP : PB = BQ : QC = CR : RD = DS : SA = 1 : n . Then the ratio of the area of PQRS to the area of ABCD is
IPMAT 2019 Question Paper - IPM Indore Quants
On a circular path of radius 6 m a boy starts from a point A on the circumference and walks along a chord AB of length 3 m. He then walks along another chord BC of length 2 m to reach point C. The point B lies on the minor arc AC. The distance between point C from point A is
IPMAT 2019 Question Paper - IPM Indore Quants
Two points on a ground are 1 m apart. If a cow moves in the field in such a way that it's distance from the two points is always in ratio 3: 2 then
- the cow moves in a straight line
- the cow moves in a circle
- the cow moves in a parabola
- the cow moves in a hyperbola

CAT
Coaching in Chennai
CAT 2024
Classroom Batches Starting Now! @Gopalapuram and @Anna nagar
CAT Preparation Online | CAT Geometry questions Videos On YouTube
Other useful sources for Geometry Question | Geometry Triangles Circles Quadrilaterals Sample Questions
CAT Questions | CAT Quantitative Aptitude
CAT Questions | CAT DILR
CAT Questions | Verbal Ability for CAT
Copyrights © All Rights Reserved by 2IIM.com - A Fermat Education Initiative.
Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions
CAT® (Common Admission Test) is a registered trademark of the Indian Institutes of Management. This website is not endorsed or approved by IIMs.
Where is 2IIM located?
2IIM Online CAT Coaching
A Fermat Education Initiative,
58/16, Indira Gandhi Street,
Kaveri Rangan Nagar, Saligramam, Chennai 600 093
How to reach 2IIM?
Phone: (91) 44 4505 8484
Mobile: (91) 99626 48484
WhatsApp: WhatsApp Now
Email: prep@2iim.com



